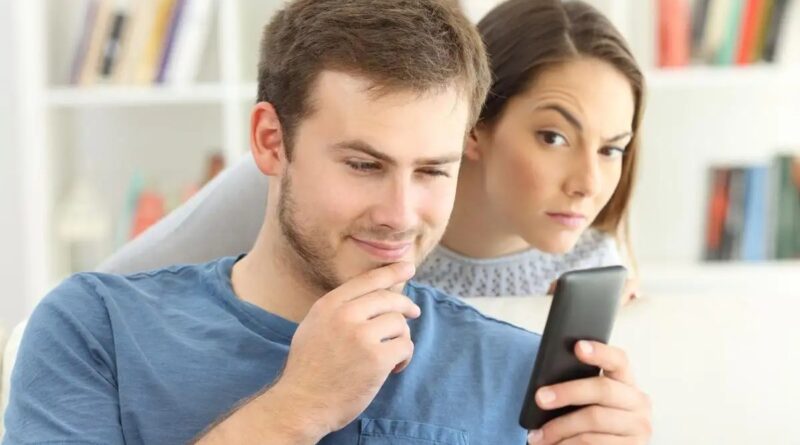
Understanding Othello Syndrome: Causes and Influences
Pathological jealousy, also known as morbid jealousy, Othello syndrome, or delusional jealousy, is a psychological condition marked by an obsessive preoccupation with the belief that a romantic partner is unfaithful, despite a lack of evidence. This irrational suspicion often leads to socially unacceptable or abnormal behavior, deeply affecting relationships and mental health.
Psychological Causes
Pathological jealousy is often linked to delusional thinking. In this state, memories can become distorted, and a partner’s innocent actions may be misinterpreted as evidence of infidelity. This cognitive distortion can convince the person of betrayal without factual basis. Brain disorders and conditions affecting cognitive function may also contribute to such delusional beliefs. Additionally, diminished sexual function, such as that experienced by an older individual with a younger partner, can trigger feelings of inadequacy and jealousy.
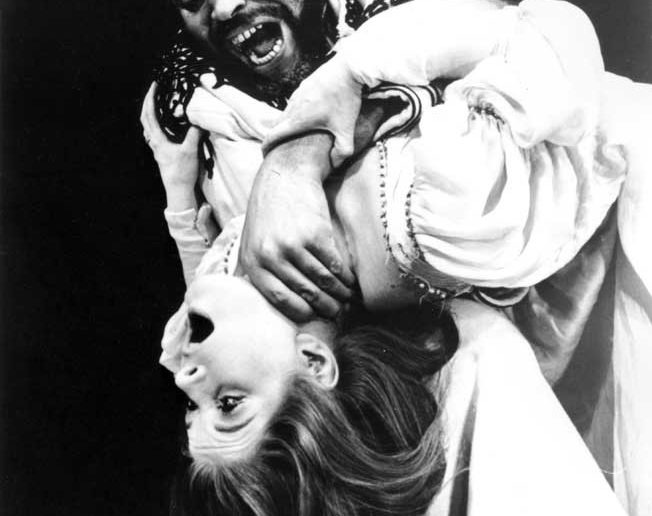

Personality Traits and Attachment
Certain personality traits make individuals more susceptible to morbid jealousy. People with insecure or fearful personalities are more prone to doubt their partner’s commitment. In particular, an insecure attachment style is strongly associated with borderline personality disorder, a condition that amplifies fears of abandonment and betrayal.
Environmental Factors
Environmental influences can also play a role in pathological jealousy. In some cases, individuals may develop irrational suspicions, such as believing they are being drugged to impair their sexual performance or accusing their partner of contracting sexually transmitted diseases through infidelity. These beliefs often stem from a combination of personal insecurities and environmental triggers.
Association with Mental Disorders
Pathological jealousy frequently coexists with other mental health conditions. It is commonly observed in individuals with schizophrenia, delusional disorder, and bipolar disorder. These conditions can exacerbate irrational fears and delusions, further complicating the individual’s ability to trust their partner.
Impact of Alcohol and Substance Abuse
There is a well-documented link between pathological jealousy and substance abuse. Drugs like amphetamines and cocaine can heighten paranoia and trigger delusions of infidelity. Even after the effects of intoxication subside, the associated delusions can persist, fueling ongoing mistrust and suspicion.
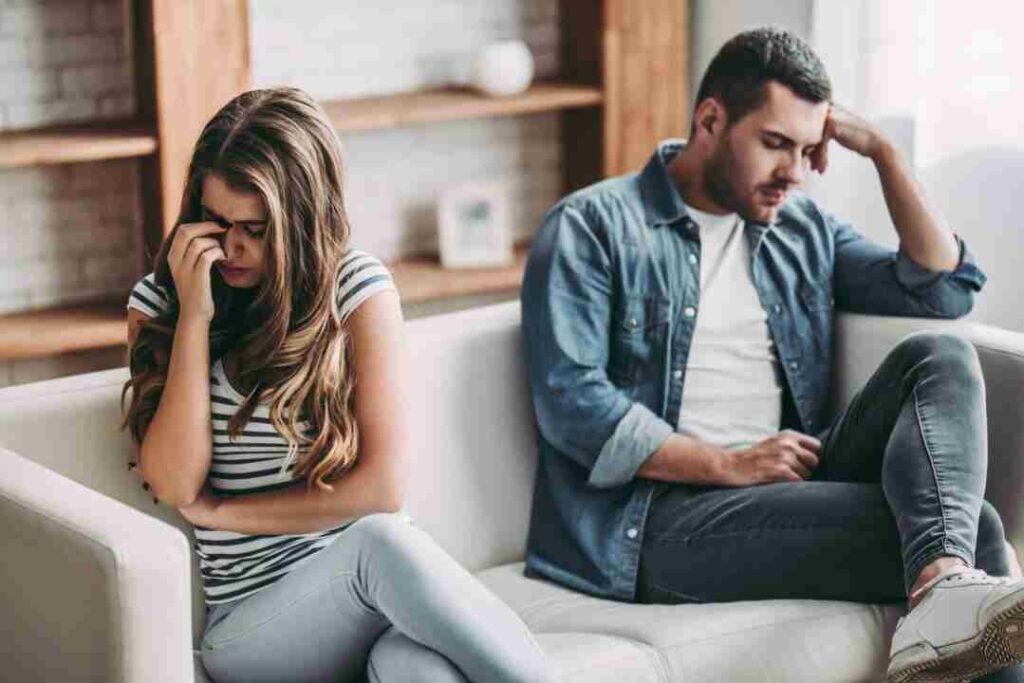

Other Contributing Factors
Several additional factors may influence the development of pathological jealousy:
- Neurological Illness: Conditions such as Parkinson’s disease have been linked to morbid jealousy due to their impact on cognitive and emotional regulation.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Individuals struggling with sexual dysfunction may experience heightened feelings of inadequacy, leading to jealousy and unfounded accusations.
Conclusion
Pathological jealousy is a complex condition with psychological, environmental, and physiological underpinnings. Understanding its causes and influences is essential for developing effective treatment approaches. Addressing underlying mental health issues, managing substance abuse, and fostering secure attachment styles are critical steps toward helping individuals overcome this debilitating condition.